Heat Capacity Worksheet
Back to the other Thermodynamics Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What is molar heat capacity?
- What is specific heat capacity?
- The kinetic energy of a system is directly related to its temperature. So if we heat a
system we its kinetic energy.
- What are two conditions under which a gas can be heated?
- What are the values for:
- Cp
- Cv
- Why is Cv<Cp?
- When energy is added to a molecule there are three potential forms of motion that it can be transferred into:
- is the only motion that directly affects temperature.
- The values 3/2 R and 5/2 R are only applicable to ideal gases. Why?
- This means that the calculated molar heat capacities are often than actual molar heat capacities.
- What equation relates ΔE to heat capacity?
- Under what conditions can you use this equation?
- Under what conditions does ΔE = q?
- What equation relates ΔH to heat capacity?
- Under what conditions can you use this equation?
- Under what conditions does ΔH=q?
- Which value of R do we use in these equations?
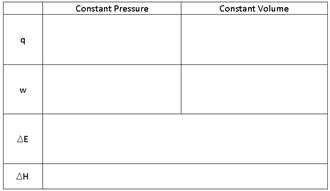
- Fill in the chart….
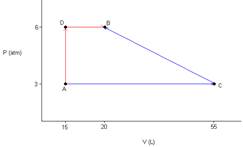
- Consider a sample containing 5 moles of a monatomic ideal gas that is taken from State Aà State B by 2 different paths. For each step, assume that the external P is constant and equals the final P of the gas for that step. Calculate the values of q, w, ΔH and ΔE for each step along the 2 paths and the totals for the 2 paths. What do the totals demonstrate?