Vapor Pressure Worksheet
Back to the other Solution Chemistry Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What is Vapor Pressure?
- Can a solute affect the vapor pressure of a solvent?
- What do solutes do to the vapor pressure of the solvent?
- How does it lower vapor pressure of solvent?
- What are two categories of solute?
- What is Raoult’s Law for this type of solute?
- What is Raoult’s Law for this type of solute?
- What type of solution obeys Raoult’s Law?
- How does an ideal solution differ from a non ideal solution?
- How do these interactions affect the predictions of Raoult’s Law?
- Label which of the following graphs obeys Raoult’s Law, which has strong exothermic interactions and which has endothermic interactions that cause a deviation from Raoult’s Law.

- Give an example of each type of interaction
-
-
- When pure methanol is mixed with water, the solution gets warmer to the touch. Would you expect this solution to be ideal? Why or why not?
- Given
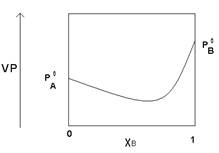
Which of the following statements is false concerning solutions of A and B?
- The solutions exhibit negative deviations from Raoult’s Law.
- ∆Hmix for the solutions should be exothermic.
- The intermolecular forces are stronger in solution than in either pure A or B.
- Pure liquid B is more volatile than pure liquid A.
- The solution with χB = 0.6 will have a lower boiling point than either pure A or pure B.
- Which of the following will have the lowest total vapor pressure at 25oC? Which has the highest vapor pressure at 25oC? At 25oC, the vapor pressure of pure water is 23.8 torr.
- Pure water.
- A solution of glucose in water with χglucose = 0.01
- A solution of sodium chloride in water with χNaCl = 0.01
- A solution of methanol in water with χmethanol = 0.2
(at 25oC, the vapor pressure of pure methanol is 143 torr)
- Glycerin (C3H8O3) is a nonvolatile liquid. What is the vapor pressure of a solution made by adding 164 g of glycerin to 338 mL of H2O at 39.8°C? The vapor pressure of pure water at 39.8°C is 54.74 torr and its density is 0.992 g/cm3.
- At a certain temperature the vapor pressure of pure benzene (C6H6) is 0.930 atm. A solution was prepared by dissolving 10.0 g of a non-dissociating, nonvolatile solute in 78.11 g of benzene at that temperature. The vapor pressure of the solution was found to be 0.900 atm. Assuming that the solution behaves ideally, determine the molar mass of the solute.
