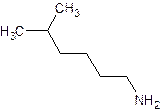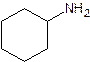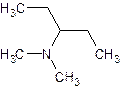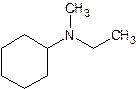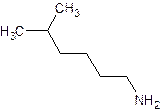Amines Worksheet - Answer Key
- The common name of an amine consists of the names of the alkyl groups bonded to the nitrogen, in alphabetical order, followed by “amine”. (Note that the entire name is written as one word)
- For the systematic naming, use the suffix “amine” to denote the amine functional group. The “e” at the end of the name of the parent hydrocarbon is replaced by “amine”. A number identifies the carbon to which the nitrogen is attached. The number can appear before the name of the parent hydrocarbon (the longest carbon continuous carbon chain attached to the amine group) or before “amine”.
- Name: 1 - hexanamine
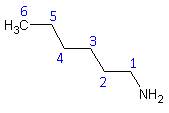
- The name of any alkyl group bonded to the nitrogen is preceded by an “N” to indicate that the group is bonded to a nitrogen rather than a carbon.
- Name: N, N – diethyl – 1 – propanamine
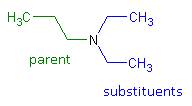
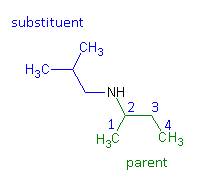
- The substituents – regardless of whether they are attached to the nitrogen or to the parent hydrocarbon – are listed in alphabetical order. Each assigned either a number or “N” denoting its location.
- Name N – (2 – methylpropyl) – 2 - butanamine
- The chain is numbered in the direction that gives the functional group the lowest number.
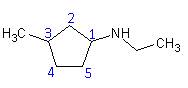
- Name: N – ethyl – 3 – methylcyclopentanamine
- What is a primary, secondary and tertiary amine?
- Give the common (if there is one) and systematic name of the following. Also indicate whether it is a primary, secondary or tertiary amine.
- Cyclohexanamine
primary
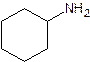
- N, N – dimethyl – 3 - pentanamine
tertiary
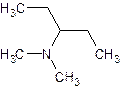
- N – ethyl – N – methylcyclohexanamine
tertiary
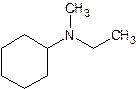
- 5 – methyl – 1 – hexanamine
primary