Alkanes Worksheet - Answer Key
- Determine the number of carbons in the longest continuous chain. This is the parent hydrocarbon (“last name”).
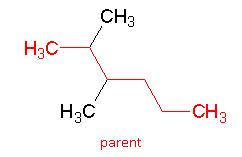
As this chain is six carbons long, the parent name is: hexane
- Any groups that are not part of the chain continuous chain are substituents. Number the chain in the direction that gives the substituent the lower number. Number are used for systematic names only (never for common names).
- Name: 2 3 - dimethylhexane
- Substituents are listed in alphabetical order. A number and word are separated by a hyphen: numbers are separated by commas. Prefixes like di, tri and tetra are ignored when alphabetizing.
- Name: 2 , 2 – dimethyl – 4 – propyloctane
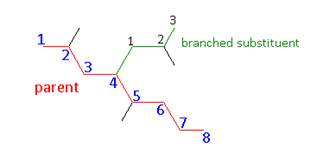
- If the substituent is a branched chain then you will need to use further specialized naming.
- Name: 2,4 – dimethyl – 4 – (2 – methylpropyl)octane
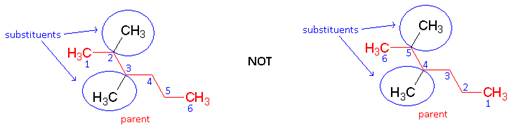
- Only if the same set of numbers is obtained in both directions does the first group cited get the lower number.
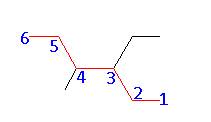
- Name: 3 – ethyl – 4 – methylhexane

Regardless of the direction numbered, the substituents are on the 3 and 4 carbon of the parent chain. In this case, take a look at the substituents. In this example we have ethyl and methyl. Because ethyl comes first (alphabetically) we will preferentially give it the lower number.
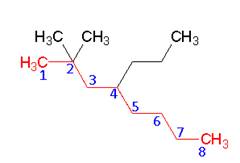
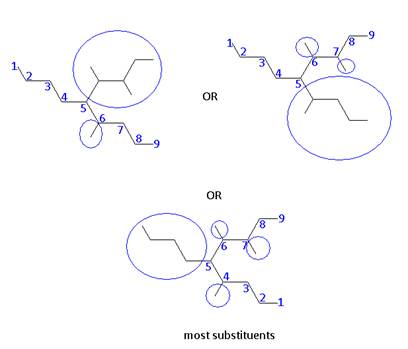
- In the case of two hydrocarbon chains with the same number of carbons, choose the parent to be one with more substituents.
- Name: 5 – butyl – 3, 4, 6 – trimethylnonane
This means that the parent chain is:
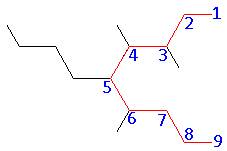
- Give the systematic name for the following:
- Name: 4 – ( 1,1 – dimethylethyl)octane
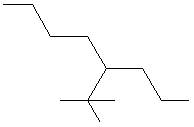
- Name: 2,2 – dimethyl – 4 – propylheptane
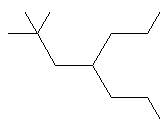
- Name: 3,3 – diethyl – 4 – methyl – 5 – propyloctane
CH3CH2C(CH2CH3)2CH(CH3)CH(CH2CH2CH3)2










