Solutions Chemistry Practice Test Part 2
Back to the other Solutions Chemistry Practice Tests and other General Chemistry Practice Tests
Go To -> Practice Test - Answer Key
- A solution is prepared from 0.0200 mol of hexane and 0.0300 mol of isopropanol. Assuming the solution is ideal; calculate the vapor pressure at 25oC. (Vapor pressure of hexane = 150.0 torr; vapor pressure of isopropanol = 44 torr at 25oC).
- 4.32 torr
- 86.4 torr
- 107.6 torr
- 92.2 torr
- 74.5 torr
- The actual vapor pressure of the sol’n in question 3 was determined to be 92.3 torr. According to Raoult’s law this solution exhibits:
- Positive deviation
- Negative deviation
- Hydrophobic deviation
- Hydrophilic deviation
- Ideal deviation
- When 236.0 mL of 0.830 M HCl is diluted with 141.0 mL of water, the molarity of the solution (assuming volumes are additive) is
- 0.310 M
- 0.00220 M
- 0.520 M
- 1.39 M
- 0.128 M
- Seawater contains 1.94% chlorine (by mass). How many grams of chlorine are there in 400 mL of seawater if the density of seawater is 1.025 g/cm3.
- What concentration of sodium chloride in water is needed to produce an aqueous solution isotonic with blood (∏ = 7.7 atm at 25°C)?
- A solution contains 1 mol of liquid A and 3 mol of liquid B. The vapor pressure of this solution is 314 torr at 25oC. At 25oC, the vapor pressure of liquid A is 265 torr and the vapor pressure of liquid B is 355 torr. Which of the following is true?
- This solution exhibits a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law.
- This solution exhibits a negative deviation from Raoult’s Law.
- This solution is ideal.
- 0.9 moles of CH2Cl2 and 7.5 moles of CH2Br2 combine to form an ideal solution. At 25oC, the vapor pressure of pure CH2Cl2 is 133 torr and the vapor pressure of pure CH2Br2 is 11.4 torr. Calculate the mole fraction of CH2Cl2 in the vapor phase at 25oC.
- 0.11
- 0.42
- 0.58
- 0.89
- None of these
- Would you expect a mixture of (C3H6O) and water to increase, decrease or maintain temperature?
- If a solution has a positive deviation from Raoult’s law, how would the boiling point change, if at all?
- Given:
1.5M KI, 1.0M NaCl, 2.0M HNO2, 2.0M NaBr, 1.5M CaCl2
Which solution would have the
- Lowest freezing point?
- Highest boiling point?
- Greatest Vapor pressure?
- The freezing point (Tf) for t-butanol (C4H9OH) is 25.50oC, and Kf is 9.1oC/m. Usually t-butanol absorbs water on exposure to the air. If the freezing point of a 13.7 g sample of t-butanol is measured at 24.89oC, how many grams of water are present in the sample?
- 0.022 g
- 0.017 g
- 0.20 g
- 0.80 g
- 7.3 g
- When the vapor pressures reach equilibrium for the following
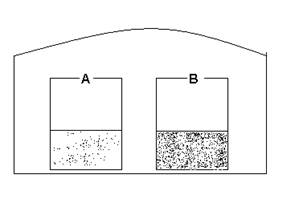
- The volumes are equal.
- Beaker A is empty
- Beaker B is empty
- Greater volume in A than B.
- Greater volume in B than A.
- A solid mixture contains MgCl2 (molar mass = 95.218 g./mol) and NaCl (molar mass = 58.443 g/mol). When 0.5000 g of this solid is dissolved in enough water to form 1.000 L of solution, the osmotic pressure at 25.0oC is observed to be 0.3950 atm. What is the mass percent of MgCl2 in the solid (assume ideal behavior for sol’n).
- A 1.60 g sample of a mixture of naphthalene (C10H8) and anthracene (C14H10) is dissolved in 20.0 g of benzene (C6H6). The freezing point of the solution is is 2.81oC. What is the composition of the sample mixture in terms of mass percent? The freezing point of benzene is 5.51oC and Kf is 5.12 oC kg/mol.
- An open beaker of saline solution is left out on your lab bench. The vapor pressure of the solution would __________ as time proceeded.
- Increase
- Decrease
- Remain the same
- The vapor pressure of carbon tetrachloride CCl4, is 0.354 atm and the vapor pressure of chloroform, CHCl3, is 0.526 atm at 316 K. A solution is prepared from equal masses of these two compounds at this temperature. Calculate the mole fraction of the chloroform in the vapor above the solution. If the vapor above the original solution is condensed and isolated into a separate flask, what would the vapor pressure of chloroform be above this new solution?
- The term proof is defined as twice the percent by volume of pure ethanol in solution. Thus, a solution that is 95% (by volume) ethanol is 190 proof. What is the molality of ethanol in a 92 proof ethanol/water solution?
Density of ethanol 0.80 g/cm3
Density of water 1.0 g/cm3
Molecular wt. of ethanol 46 g/mol
- True or False: We can predict the solubility of a compound by looking at the sign of the enthalpy of solution.
- Which of the following statements is(are) true?
- The rate of dissolution of a solid in a liquid always increases with increasing temperature.
- The solubility of a solid in a liquid always increases with increasing temperature.
- According to Henry's law, the amount of gas dissolved in a solution is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the liquid.
- Two of these statements are true.
- All of these statements are true.
- For each of the following solutions, would you expect it with respect to Raoult's law to be relatively ideal, to show a positive deviation, or to show a negative deviation?
- hexane (C6H14) and chloroform (CHCl3)
- water and acetone (C3H6O)
- hexane (C6H14) and octane (C8H18)
- When a nonvolatile solute is added to a volatile solvent, the solution vapor pressure __________, the boiling point __________, the freezing point __________, and the osmotic pressure across a semi-permeable membrane __________.
- A 0.2 molar solution of a solute X, in benzene, displays an osmotic pressure given by the formula = (0.1)RT. Which of the following is most likely to be the case?
- X exists in benzene as X.
- X exists in benzene as X2.
- X exists in benzene dissociated into two particles.
- This solution strongly deviates from ideal behavior.
- If the human eye has an osmotic pressure of 8.45 atm at 25°C, what concentration of solute particles in water will provide an isotonic solution?
- 0.346 M
- 4.11M
- 3.49 x 10-3 M
- 4.04 x 10-2 M
- 0.673 M
- The solubility of the salt MxAy is 1.0 10-2 mol/L at 25°C. The osmotic pressure exhibited by a solution saturated with MxAy at 25°C is 1.22 atm. Determine the values of x and y by assuming ideal behavior.
- x = 1, y =3
- x = 2, y = 5
- x = 2, y = 3
- x = 1, y = 1
- What is the molar mass of glucose if 22.5 g gives a freezing point of –0.930°C when dissolved in 250.0 g of water? If the empirical formula is CH2O, what is the molecular formula? (Kf=1.86 C kg/mol)
- An aqueous solution is 1.00% NaCl by mass. Its density is 1.071 g/mL at 25°C. The observed osmotic pressure of this solution is 7.83 atm at 25°C.
- What fraction of the moles of NaCl in this solution are ion pairs?
- Calculate the freezing point that would be observed for this solution; Kf for H2O = 1.86° C kg/mol.
- In the vapor over a pentane – hexane solution at 25oC, the mole fraction of pentane is equal to 0.15. What is the mole fraction of pentane in the solution? The vapor pressure of pure pentane and hexane are 511 and 150. torr respectively.
- Which of the following aqueous solutions is expected to have the largest Van’t Hoff factor?
- 0.10 m I2
- 0.10 m NaCl
- 0.10 m K2SO4
- 0.01 m K2SO4
- For which of the following solutions would one be most likely to expect a positive deviation from Raoult’s Law?
- Octane and 1-butanol
- Propanone and water
- Pentanal and ethanoic acid
- More than one of these
- None of these
- An aqueous solution contains 0.250 moles of Q, a strong electrolyte, in 5.00 x 102 g of water freezes at -2.79 oC. What is the van’t Hoff factor for Q? The molal freezing point depression constant for water is 1.86 oC kg/mol. What is the formula of Q if it is 38.68% chlorine by mass and there are twice as many anions as cations in one molecule.
- You have a solution of two volatile liquids, A and B (assume ideal behavior). Pure liquid A has a vapor pressure of 350.0 torr and pure liquid B has a vapor pressure 100.0 torr at the temperature of the solution. The vapor at equilibrium above the solution has double the mole fraction of substance A as the solution does. What is the mole fraction of liquid A in the solution?
