Phase Changes Practice Test - Answer Key
Back to the other Phase Changes Practice Tests and other General Chemistry Practice Tests
Go To -> Practice Test - Answer Key
- A certain substance, X, has a triple-point temperature of 20oC at a pressure of 2.0 atm. Which of the following statements cannot possibly be true?
- X can exist as a liquid above 20oC
- X can exist as a solid above 20oC
- Liquid X can exist as a stable phase at 25oC, 1 atm.
- Both liquid and solid X have the same vapor pressure at 20oC.
- All these statements could be true.
- The density of the solid phase of a substance is 1.0 g/cm3 and the density of the liquid phase is 0.9 g/cm3. A large increase in pressure will
- Lower the freezing point.
- Raise the freezing point.
- Lower the boiling point.
- Raise the triple point.
- Lower the triple point.
- When a substance is condensed from a gas directly to a solid, what are the signs of ∆H and ∆S, respectively?
- Positive, positive
- Positive, negative
- Negative, positive
- Negative, Negative
- ∆H = 0, positive
- True or False.
At the meting point, the vapor pressure of the liquid must be greater than the vapor pressure of the solid.
- The triple point of iodine is at 90 torr and 115oC. This means that liquid I2
- Is more dense than I2 (s).
- Cannot exist above 115oC.
- Cannot exist at 1 atm pressure.
- Cannot have a vapor pressure less than 90 torr.
- Can exist at a pressure of 10 torr.
- The heat of vaporization of a certain refrigerant is 149 J/g. Calculate the number of kilograms of refrigerant that must be evaporated to freeze a tray of 18, one-ounce (1oz = 28g) ice cubes with the water at 13oC.
Cwater = 4.184 J/goC ∆Hfusion (water) = 333 J/g
- 0.18 kg
- 0.94kg
- 1.2 kg
- 4.7 kg
- 1.3 kg
- Shown below is a phase diagram for sulfur (not to scale). Sulfur can exist in two solid modifications, rhombic and monoclinic, denoted by SR and SM, respectively. Which one of the following statements is incorrect.
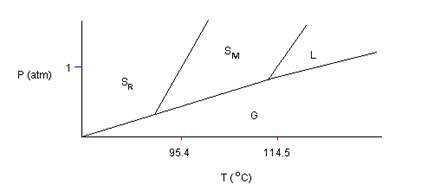
- The density of liquid sulfur is less than monoclinic sulfur.
- Under ordinary atmospheric conditions, sulfur does not sublime.
- At pressure close to 1 atm, rhombic sulfur can be in stable equilibrium with liquid sulfur.
- At a given pressure, there is (at most) one temperature at which rhombic sulfur can exist in equilibrium with monoclinic sulfur.
- None of the above are incorrect.
- 81.4 kJ of energy exactly vaporizes all the water from a sample at 100oC. ∆Hvap = 40.7 kJ/mol. How much water was there to start with?
- 18g
- 36g
- 40.7g
- 81.4g
- 2g
- How much energy is needed to convert 58.4 grams of steam at 110.00°C to ice at 0.0°C?
Specific heat of steam = 2.02 J/(g°C)
Specific heat of water = 4.18 J/(g°C)
Heat of fusion = 333 J/g
Heat of vaporization = 2258 J/g
E = –177 kJ
- Based on the phase diagram shown below, which of the following statements are correct?
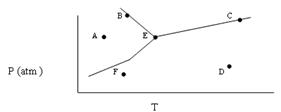
- Sublimation occurs at a point in the transformation that falls along a straight line from point A to point F.
- C and E represent points where the gas and liquid phases are in equilibrium.
- Molecules at point D have a greater average kinetic energy than those at point F.
- The temperature at point E is called the critical temperature of the compound.
- Consider the following data for xenon:
Triple point -121oC, 280 torr
Normal Melting Point -112oC
Normal Boiling Point -107oC
Which is more dense, Xe(s) or Xe(l)?w
- The melting point of a fictional substance X is 225oC at 10.0 atm. If the density of the solid phase of X is 2.67 g/cm3 and the density of the liquid phase is 2.78 g/cm3 at 10.0 atm, predict whether the normal melting point of X will be less than, equal to, or greater than 22.5oC.
Greater
