Chemical Kinetics Practice Test
Back to the other Chemical Kinetics Practice Tests and other General Chemistry Practice Tests
Go To -> Practice Test - Answer Key
- When 0.52 g of H2 and 0.19 g of I2 are confined to a 750. mL vessel heated to 700. K, they react by a second order process (first order in each reactant), with k = 0.063 L mol -1 s -1 in the rate law ( for the rate of formation of HI).
- What is the initial reaction rate?
- By what factor does the reaction increase if the concentration of H2 present in the mixture double?
- The following rate data were collected for the reaction
2 A(g) + 2 B(g) + C(g) → 3G(g) + 4 F(g)
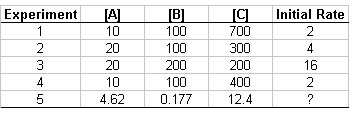
- What is the order for each reactant and the overall order of the reaction?
- Write the rate law for the reaction?
- Determine the reaction rate constant.
- Predict the initial rate for Experiment 5.
- A first order reaction is 38.5% complete in 480 s.
- Calculate the rate constant.
- What is the value of the half-life?
- How long will it take for the reaction to be 75.0% complete?
- One pathway for the destruction of ozone in the upper atmosphere is
Step 1 O3 + NO → NO2 + O2
Step 2 NO2 + O → NO + O2
- Write the overall reaction.
- What are the reaction intermediates?
- What are the catalysts?
- A proposed mechanism for a reaction is:
C4H9Br → C4H9+ + Br - Slow
C4H9+ + H2O → C4H9OH2+ Fast
C4H9OH2+ + H2O → C4H9OH + H3O+ Fast
Write the rate law expected for this mechanism?
- Consider:
2CH3OH(g) + 3O2 (g)→ 2CO2 (g) + 4H2O (l)
At certain temperatures it obeys the rate law:
Rate = 5.30 M -1 s -1 [CH3OH]2
Suppose a vessel contains CH3OH at a concentration of 1.83 M. Calculate the concentration of the CH3OH in the vessel 0.968 seconds later.
- If the rate law was determined to be
Rate = k[A]-0.8[B]3.1
What are the units for k?
- What is the 2nd half-life for a reaction with k = 15 M -1 s‑1 and an initial concentration of 16M?
- The reaction profile for the mechanism
NO2 (g) + F2 (g) → NO2F(g) + F (g) Slow
F (g) + NO2 → NO2F (g) Fast
Shows
- 2 maxima, the second maximum being higher than the first
- One maximum for the first step
- 2 maxima of the same heights
- One maximum for the second step
- 2 maxima, the first one higher than the second one.
- The rate constant of the first order reaction
2 N2O (g) → 2 N2 (g) + O2 (g)
is 0.76 s -1 at 1000. K and 0.87 s -1 at 1030 K. Calculate the activation energy of the reaction.
- Complete the following statements relating to the following overall reaction:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) - The rate of N2 is __________ times the rate of consumption of H2.
- The rate of formation of NH3 is __________ times the rate of consumption of H2.
- The rate of formation of NH3 is __________ times the rate of consumption of N2.
- The first order reaction A → 3B + C, when [A]o =0.015 M, the concentration of B increases to 0.018 M in 3.0 min.
- What is the rate constant for the reaction expressed as a rate loss of A?
- How much more time would be needed for the concentration of B to increase to 0.030 M?
- Determine the rate law for the following reaction
Cl2 (g) + CHCl3 (g) → HCl(g) + CCl4 (g)
Given the following mechanism:
Cl2 (g)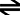 2Cl (g) Fast Equilibrium
2Cl (g) Fast Equilibrium
Cl (g) + CHCl3 (g) → HCl (g) + CCl3 (g) Slow
CCl3 (g) + Cl (g) → CCl4 (g) Fast
