State vs. Path Functions Worksheet - Answer Key
Back to the other Thermodynamics Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key
- What is a state function?
A function that depends only on the values of initial and final conditions. The method taken to get from the original value to the final value has no bearing. Examples of states functions are:
∆T (change in temperature), ∆V (change in volume), ∆P (change in pressure), and ∆E (change in internal energy). We will find more state functions as we proceed through thermodynamic.
- Examine the following:
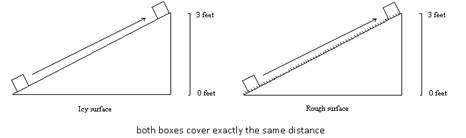
Compare values of w, q and ΔE for each.
Because of frictional forces, there would be a different amount of work and heat for each incline. They would, however, have exactly the same ∆E. Both boxes started and ended at exactly the same place – this would mean that they would have exactly the same change in potential energy, as it only depends on position – not on how the change occurred.
- Based on the above, we can conclude that
- Heat and work are dependent on path; meaning they are path functions.
- Internal energy is independent of path; meaning it is a state function.
- What are some additional examples of state functions?
ΔH, ΔS, ΔG, ΔV, ΔT, ΔP, etc.
