Kinetic Molecular Theory
Back to the other Gases Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What are the postulates of the kinetic molecular theory?
- From this information under what conditions would real gases behave similarly to ideal gases?
- What is the equation for Average Kinetic Energy?
- What does kinetic energy describe?
- How does temperature effect kinetic energy?
- What is the equation for the root mean square velocity?
- How does mass affect the velocity?
- How does temperature affect the velocity?
- Consider:
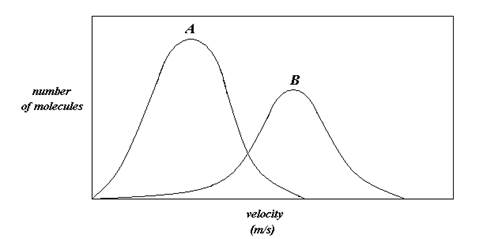
- If the plot represents the velocity distribution of 1.0 L of H2 (g) versus 1.0 L of Ar (g) at STP, which plot corresponds to each gas?
- If the plots correspond to the velocity distribution of 1.0 L of O2 (g) at 273K and 1273K, which plot corresponds to each temperature?
- Under which temperature condition would the O2 (g) behave most ideally?
- What is diffusion?
- What is effusion?
- What is Graham’s Law?
- It took 5.3 minutes for 1.0 L of helium to effuse through a porous barrier. How long will it take for 1.0L of chlorine gas to effuse under identical conditions?
- Consider the following equations

How would the following affect number of collisions and length of mean free path?
- Increase in mass?
- Increase in diameter of particle?
- Increase concentration of gas?
- What is the Van Der Waal’s Equation?
- What is it correcting for?
- What does the variable “a” have to do with?
- What does the variable “b” have to do with?
- Would He(g) or H2O(g) have a greater value of “a”?
- Would He(g) or Xe(g) have a smaller value of “b”?
