Le Chatelier's Principle Worksheet - Answer Key
Back to the other Equilibrium Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What is Le Châtelier’s Principle?
Le Châtelier’s Principle states that if a change in conditions is imposed on a system at equilibrium, and that change pushes the system out of equilibrium, the reaction will shift to the direction that reduces the effects of that change.
- How can you cause changes in the following? How does a change in them affect equilibrium?
- Concentration
Concentration can be changed by adding or subtracting moles of reactants/products.
If a gaseous/aqueous reactant or product is added to a system at equilibrium, the system will shift away from the added component.
If a gaseous/aqueous reactant or product is removed from the system at equilibrium, the system will shift toward the removed component.
- Pressure
Pressure can be change by:
1. Adding or subtracting moles of gaseous reactants/products at
constant volume.
The system will behave in the same way as above.
2. Increasing/decreasing the volume of the container.
When the volume of the container holding a gaseous system is reduced, the system responds by shifting in the direction that results in fewer moles of gas.
When the volume of the container holding a gaseous system is increased, the system responds by shifting in the direction that results in a great number of moles of gas.
3. Adding an inert (non-reactive) gas at constant volume.
There will be no shift in this system; this is because the system is never pushed out of equilibrium.
- Temperature
The temperature is changed by increasing or decreasing the heat put into the system.
To understand how a reaction will be affected by this type of change – you must know whether the reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
Exothermic: This means that heat is released by the reaction (you
can picture heat as being a product).
Endothermic: This means that heat is absorbed by the reaction (you
can picture heat as being a product).
Once you have established exothermicity or endothermicity you will treat the problem in the same way as changes in concentration.
Adding heat results in a shift away from heat.
Removal of heat results in a shift towards heat.
- Why does a change in pressure caused by volume change result in a shift but not a pressure change cause by an inert gas addition?
Kp is based on partial pressures. If you change the partial pressures of the gases in the reaction you shift out of equilibrium.
When you add an inert gas into the reaction vessel, the total pressure is increased but the partial pressures of the gases involved in the reaction never changes. This means that the reaction never comes out of equilibrium so a shift is unnecessary.
When the volume of the container is changed, the partial pressures of the gases involved in the reaction are changed. This means the reaction has moved away from the equilibrium. So by decreasing/increasing it’s own volume the partial pressures are brought back to a point where the values, when plugged into the equilibrium constant expression, yields Kp.
- Consider:
2 NBr3 (s)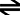 N2 (g) + 3 Br2 (g)
N2 (g) + 3 Br2 (g)
How would the reaction shift if…
- The concentration of N2 is decreased?
The reaction would shift to the right (toward the N2) in order to bring the reaction back to its equilibrium position.
- The concentration of Br2 is increased?
The reaction would shift to the left (away from the Br2) in order to bring the reaction back to its equilibrium position.
- The amount of NBr3 is doubled?
No shift. NBr3 is a solid; solids do not affect the equilibrium position, thus no shift is required.
- The pressure is decreased by changing the volume?
The volume would have to be increased in order to lower the pressure. This means that the reaction would have to shift right towards more moles of gas. This would result in an increase in pressure which would allow for a return to the equilibrium position.
- The pressure is increased by adding He(g)?
No shift. He(g) is not part of the reaction and therefore would not cause the system to shift out of equilibrium.
- Consider:
aA + bB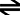 cC + dD
cC + dD
Determine if the above reaction is endothermic or exothermic based on the following information:
TEMPERATURE K
150 K 0.0053
500 K 12
2000K 65
Endothermic reaction.
