Galvanic Cells Worksheet - Answer Key
Back to the other Electrochemistry Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What is a galvanic cell?
A cell that utilizes the spontaneous electron transfer that occurs in a redox reaction to create electrical energy.
- Draw a galvanic cell and label all its components.
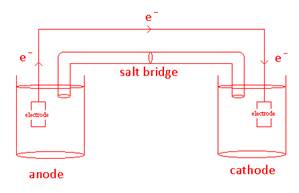
- Why is a salt bridge necessary to complete the circuit?
A salt bridge insures that there will not be a charge build up when the electrons transfer.
- What do the following acronyms mean?
- RED-CAT
REDuction at CAThode
- OX-AN
OXidation at ANode
- What is the unit measure for cell potential?
Volts (V) = Joule (J)
Coulomb (C)
- What are standard conditions?
1M concentration and 1 atm pressure
- You must break the redox reaction into half reactions in order to determine the anode and cathode.
- For a galvanic cell the value of ε°cell must be positive as it indicates spontaneity.
- What overall reaction would happen between based on the reduction potentials of each half reaction.?
- Mn2+ + 2e-→Mn ε° = -1.18V
Cu2++e-→Cu ε°=0.34V
Mn + Cu2+→ Mn2+ + Cu εo = 1.52V
- Mn2+ + 2e-→Mn ε° = -1.18V
Fe3+ + 3e-→Fe ε° = -0.036V
3Mn + 2Fe3+→ 3Mn2+ + 2Fe εo = 1.14V
- Answer the following using standard reduction potential values
- Is H+(aq) capable of dissolving Cu(s) to Cu2+(aq)?
No. - Is Fe3+(aq) capable of oxidizing I-(aq)?
Yes.
- Is H2(g) capable of reducing Ag+(aq)?
Yes.
- Is Fe2+(aq) capable of reducing Cr3+(aq) to Cr2+(aq)?
No.
- Using the standard reduction potential and considering
Na+, Cl-, Ag+, Ag, Zn2+, Zn and Pb
answer the following
- Which is the strongest oxidizing agent?
Ag+
- Which is the strongest reducing agent?
Zn
- Which species can be oxidized by SO42-(aq) in acid?
This means that any substance with a standard reduction potential less than 0.20V would be capable of being oxidized by SO42– .
- Which species can be reduced by Al(s)?
This means that any substance with a standard reduction potential greater than -1.66V would be capable of oxidizing Al.
- What equation relates ε° and ∆G°?
ΔGo = – nFεo
- What is F?
Faraday’s Constant = 96,485 C .
mol e
- What is n?
Total moles of electrons transferred.
- Just as the value of ∆G is dependent upon the concentrations of reactants/products – ε is as well. Leading to the following equations:
- For non-standard cells:
ε = εo – RT ln Q
nF
- At equilibrium:
εo = RT ln Q
nF
- Calculate the values of ∆G° and K for the following cell
H2O2 + 2H+ + 2e-→ 2H2O ε°= 1.78V
O2 + 2H+ +2e-→ H2O2 ε° = 0.68V
ΔGo = –212,000J
K = 1.62 x 1037
- Consider the following galvanic cell at 25°C:
Pt|Cr2+(0.30 M), Cr3+(2.0M)|| Co2+(0.20M)|Co K=2.79 x 107
Calculate the cell potential and ∆G for this galvanic cell.
ε = 0.15V
ΔG = –29,000 J - Consider the cell described below
Al|Al3+(1.00M)||Pb2+(1.00M)|Pb
Calculate the cell potential after the reaction has operated long enough for the [Al3+] to have changed by 0.60 mol/L. (assume T=25°C)
ε°cell = 1.50 V
