Isomers Worksheet - Answer Key
Back to the other Coordination Compounds Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What is an isomer?
Isomers are compounds with the same formula, but different chemical/physical properties.
- Complete Isomer Flow Chart

- Define and give an example of each of the following
- Coordinate Isomerism
A ligand and a counter ion switch positions.
[Cr(NH3)5Br]SO4 and [Cr(NH3)5SO4]Br
- Linkage Isomerism
This occurs when you have a ligand that has 2 or more potential areas of attachment structured in such a way that only one or the other end is able to attach at a time
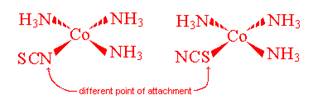
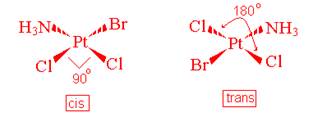
- Geometric (cis-trans) Isomerism
These isomers have two identical ligands that can either be placed 90o (called cis) or 180o (called trans) from each other.
- Optical Isomerism
This is when you have isomers that are non-super imposable mirror images. These type of isomers rotate plane polarized light in different directions.
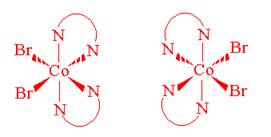
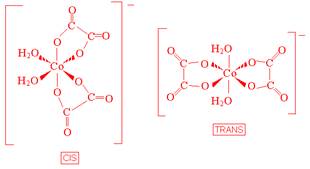
- Draw geometrical isomers of each of the following complex ions.
- [Co(C2O4)2(H2O)2]-
- [Pt(NH3)4I2]2+
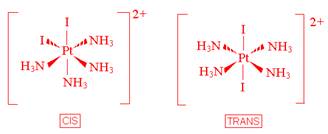
- Which of the following ligands are capable of linkage isomerism?
SCN-, N3-, NH2CH2CH2NH2, OCN-, I-
- Draw all the geometric isomers of Pt(CN)2Br2(H2O)2. Which of these isomers has an optical isomer? Draw the various optical isomers.
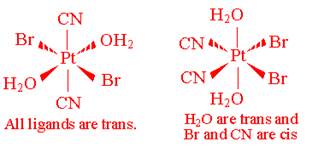

There is only one optically active isomer:
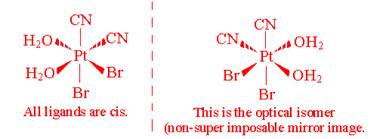
- How do you know if a complex ion, with tetrahedral geometry, is optically active?
The metal has four different ligands attached.
- In order for a molecule to be optically active it must be chiral.
- In order to be chiral a molecule must have a non-super imposable mirror images.
- Chiral isomers are called enantiomers.
- An isomer that rotates plane polarized light to the left is called levorotary (l).
An isomer that rotates plane polarized light to the right is called dextrorotary (d).
- What is a racemic mixture?
A 50/50 mixture of d/l enantiomers.
