Strong Bases vs. Weak Bases Worksheet
- Answer Key
Back to the other Acid Base Chemistry Workbooks and other General Chemistry Workbooks
Go To -> Worksheet - Answer Key - Solutions Manual
- What is the BrФnsted-Lowry defintion of a base?
A substance that accepts H+.
- What is the generalized equation for the reaction of a base in water?
B + H2O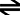 BH+ + -OH
BH+ + -OH
- What is Kb?
Kb is the equilibrium constant for a base.
- What are some characteristics of strong bases?
- Equilibrium lies so far to the right that reaction is said to go to completion.
[XOH] = [– OH]
[X(OH)2] = 2 x [– OH]
- Strong bases have very large Kb values.
- Strong bases yield conjugate acids that are weaker than water. Therefore their presence has no effect on pH.
- What are some characteristics of weak bases?
- Equilibrium lies far to the left.
- Weak bases have Kb << 1
- Weak bases yield a conjugate that is a stronger acid than water. Thus, they can affect the pH of a solution.
- How can you identify a strong base?
Strong bases are substances that have a Group 1 or 2 cation ionically bound to –OH, –NH2, –CH3, etc.
- How can you identify a weak base?
Weak bases typically contain an amine derivative (NH3, CH3NH2, etc.) or it is the conjugate base of a weak acid.
